Computer science education still has diversity gaps
Google’s Vice President of Education and Research, Maggie Johnson, recently published this blog on the latest Gallup poll investigating diversity gaps in computer science education. We’ve reprinted this with permission. You may also access statistics from the Gallup poll here.
Jobs in the computing field are expected to grow by 13 percent between 2016 and 2026, a rate that’s faster than the average growth rate for all occupations. But the latest research shows that not all K-12 students have the same access to, or perceptions of, computer science (CS) education—especially girls and Black students. COVID-19 has only exacerbated existing gaps, underscoring the need for more creative solutions to ensure all students receive the education they deserve today to succeed tomorrow, according to additional research.
To better understand these gaps and where we can focus on finding solutions, we’re continuing our funding support of Gallup’s comprehensive, multi-year research on the K-12 computer science education landscape. Today, we’re releasing Gallup’s latest findings, “Current Perspectives and Continuing Challenges in Computer Science Education in US K-12 Schools.” This report represents Gallup’s analysis of over 7,000 interviews with U.S. educators, parents, administrators and students. It is accompanied by four supplemental reports highlighting equity gaps among different segments of the population, including Black, female, Hispanic and rural students.
The research uncovered four key themes:
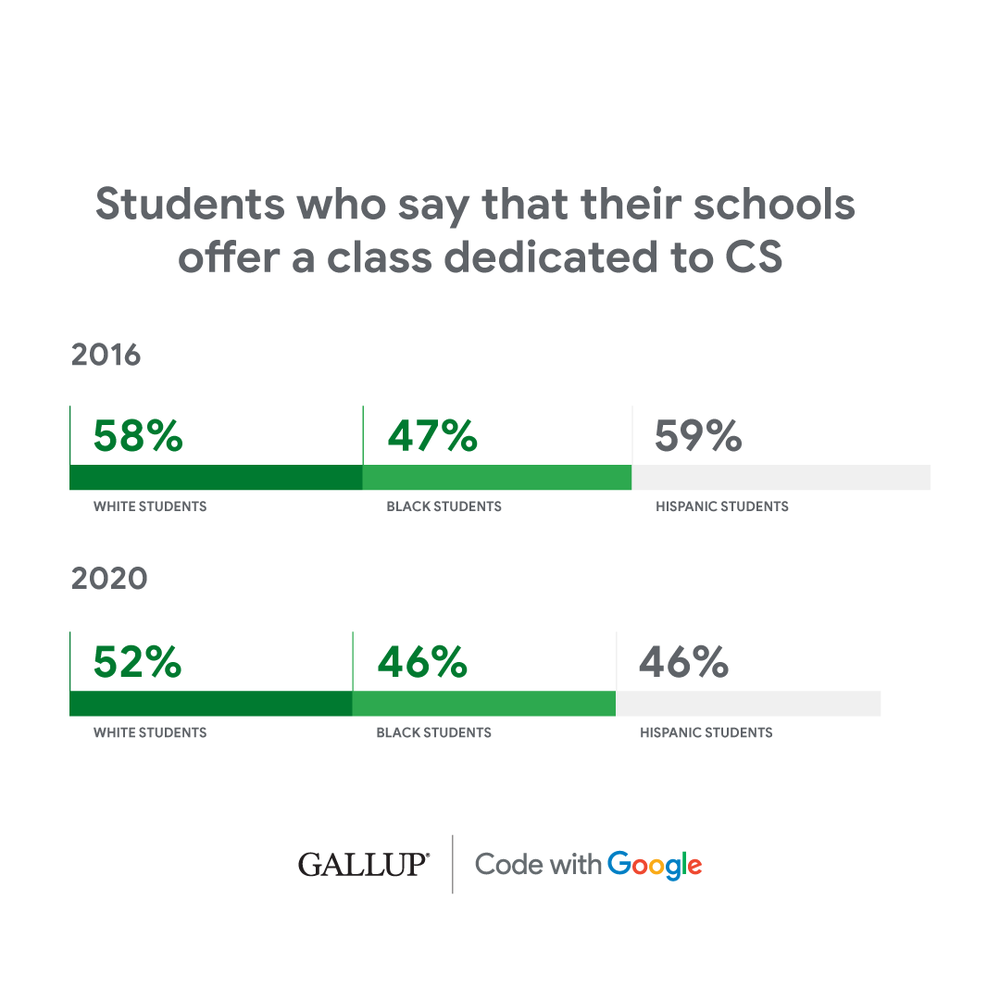
1. There are still gaps in access to computer science education between Black, Hispanic and white students.
Consistent with the 2016 study, in 2020, Gallup found only 46 percent of Black students and 46 percent of Hispanic students indicate that they have classes dedicated to computer science at their high school, compared to 52 percent of white students.
2. There’s still a significant gender gap, too.
Seventy-three percent of boys say they are confident they can learn computer science, compared with 60 percent of girls, a gender gap similar to the one observed in 2016.

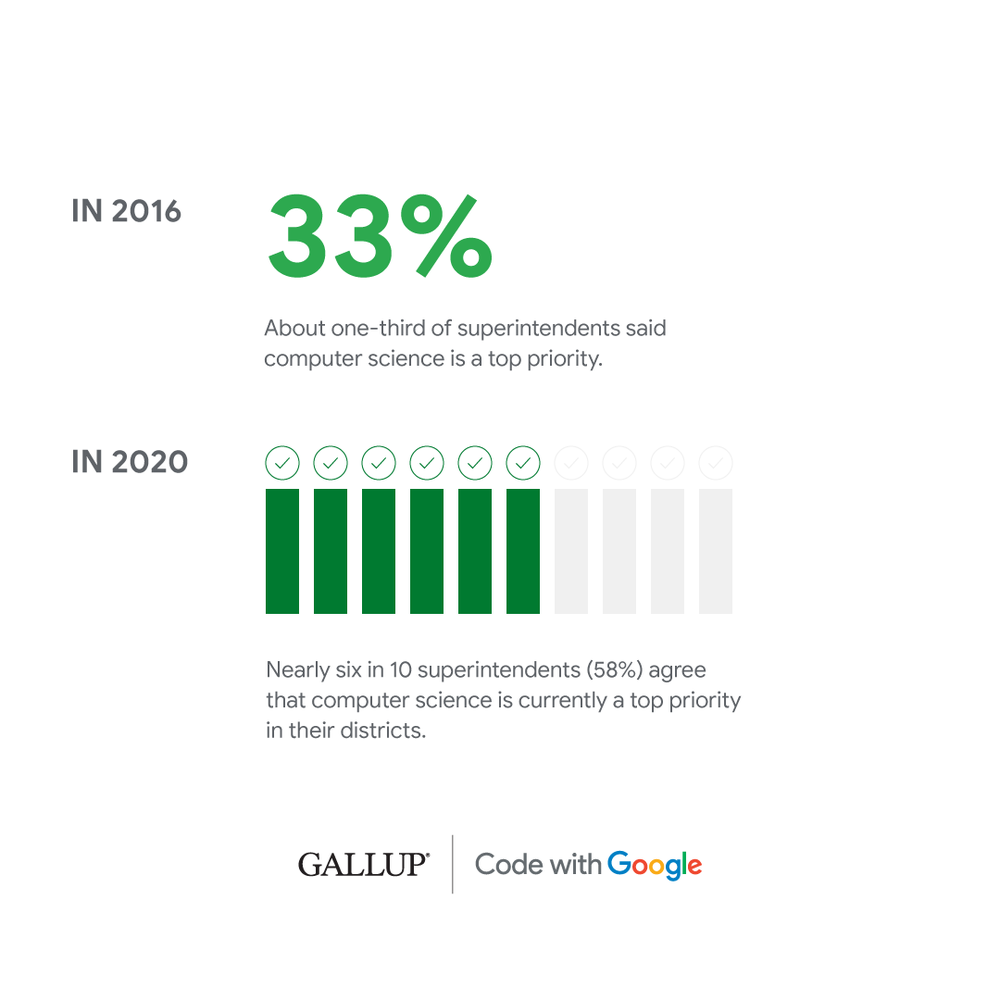
3. Computer science is a top priority for superintendents, but that same prioritization hasn’t made it to the classroom yet.
In 2020’s report, nearly six in 10 superintendents (58 percent) agree that computer science is currently a top priority in their districts. However, there appears to be a disconnect between administrators and teachers and principals, because just 18 percent of public school teachers and 28 percent of principals say computer science education is treated as a top priority at their schools.
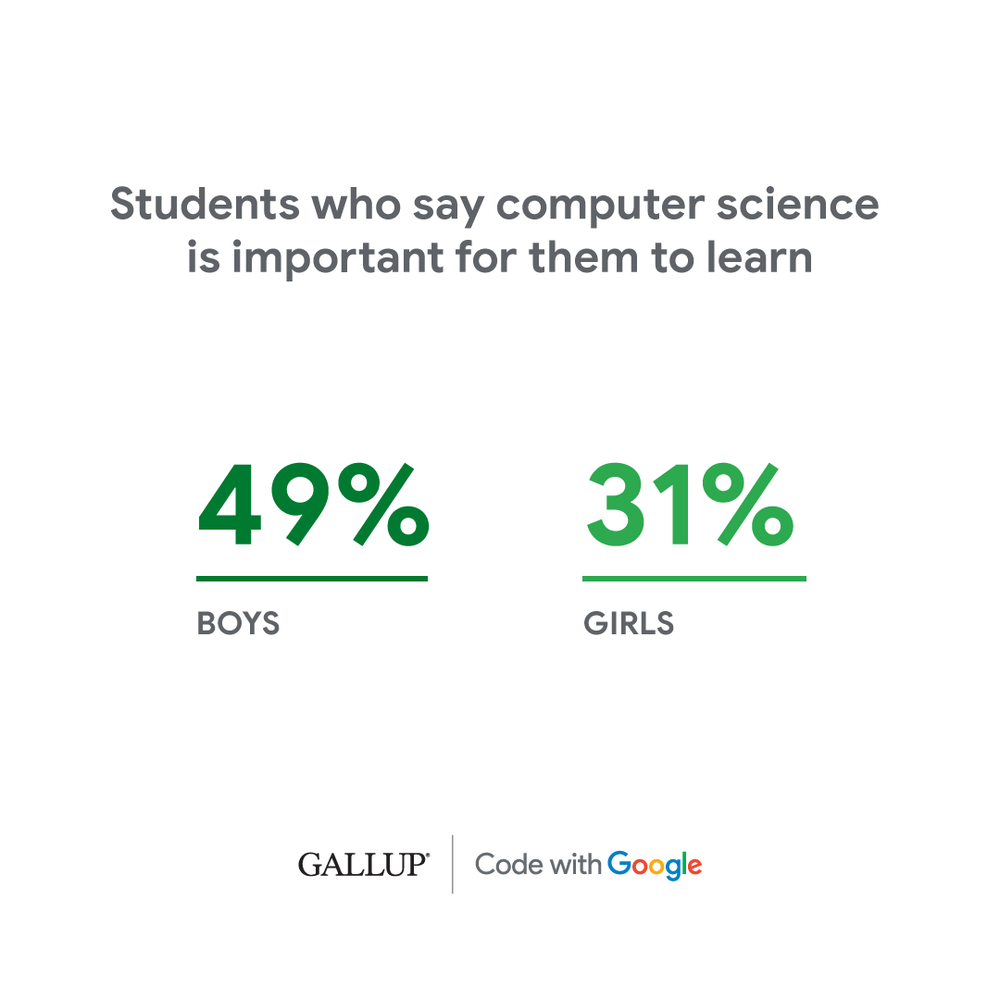
4. Students are generally unconvinced that computer science is important for them to learn.
Female students are particularly skeptical about the importance of learning computer science education, with just 31 percent of them saying CS is important for them to learn, compared with 49 percent of male students.
Interventions from parents, educators, community leaders, policymakers, nonprofits and the technology industry are needed to encourage girls, Black students and Hispanic students to take computer science courses and ensure that when that interest exists, it’s matched with high quality learning opportunities. These students also need to be shown how CS knowledge can help them meet their goals in a variety of fields including the humanities, medicine and the arts.
With over $80 million in funding from Google.org, and a variety of programs as part of Code with Google, we are committed to closing equity gaps in CS education. For example, Code Next is a free computer science education program that meets Black and Latino high school students in their own communities. As part of our Google.org funding, we also gave a $3 million grant to The Kapor Center to establish the Equitable Computer Science Curriculum initiative. This effort brings together leaders in education equity, inclusive teaching practices and CS education, along with teachers and students to improve CS curricula and resources to increase racial and gender equity in CS classrooms.
No organization can increase access or improve perceptions of computer science education alone. We’re enthusiastic about all the work from nonprofits who have developed and share culturally-relevant learning resources, educators who support all of their students with skills they need to succeed, technology companies who have dedicated resources and governments who have created new policies to address CS learning gaps over the past five years. But we at Google believe there’s more work to be done in this complex field, and we hope publishing these reports helps the entire education community continue to advocate for and support underserved students. All of this research is fully accessible and for use in presentations.
(A virtual panel discussion was held on September 30, 12 p.m. Pacific/ 3 p.m. Eastern discussing the report’s key takeaways with Stephanie Marken, Gallup’s Executive Director of Education Research, and Dr. Alexis Martin, the Director of Research Partnerships at Kapor Center.)
 Maggie Johnson is Director of Education and University Relations for Google. She manages all technical education, content development, and information management programs for Google engineers and operations staff, as well as Google’s K12 educational programs in STEM and computer science (CS).
Maggie Johnson is Director of Education and University Relations for Google. She manages all technical education, content development, and information management programs for Google engineers and operations staff, as well as Google’s K12 educational programs in STEM and computer science (CS).

Comments are closed