More than any other school-related factors that impact student achievement, it has been shown that the teacher factor has an effect size two to three times greater than that of the next most important factor \cite{opper2019teachers}. Among the attributes that teachers can develop that positively impact student academic achievement include being committed to and persistent about their students’ learning, developing their self-efficacy, and contributing to their professional support system \cite{lee2010personal}. Many of these factors’ impacts have been examined with respect to general education and specific subjects (e.g., math, literacy) \cite{shahzad2017impact, khourey2004longitudinal}, and there is some empirical evidence to date on their direct impact on students’ learning CS \cite{zhou2020high, ravitz2017early}.
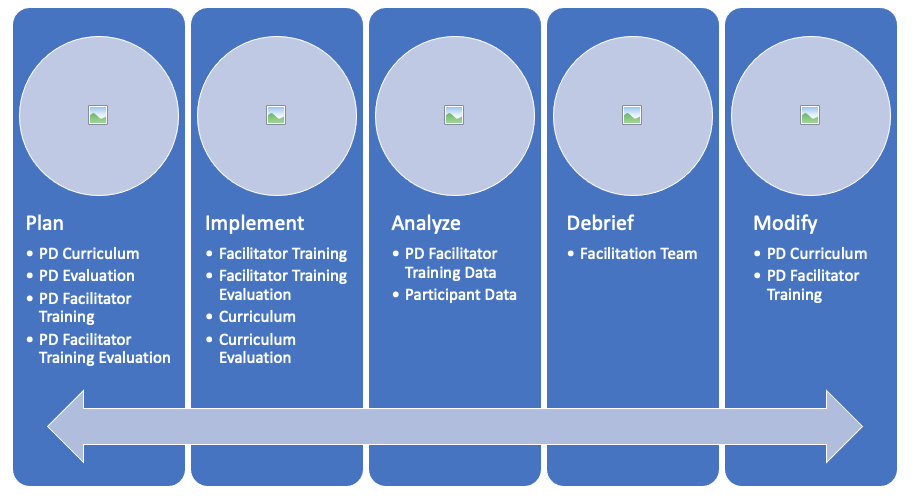
The main goal of evaluating PD is to determine whether your PD is effective in meeting its planned goals so that changes can be made to improve the PD. This follows the continuous improvement model’s Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) method, where evaluation is the “Check” and making changes to your PD is the “Act”.
A Teacher’s Impact on Student Learning and Growth
Teacher factors related to student academic achievement go well beyond content knowledge. Teacher self-efficacy, mindset and pedagogical content knowledge, for example, are critical for student growth (citations). Each district and school community also has their own set of needs and values, which local PD providers should be aware of and align evaluation accordingly (citation).
Key questions to consider when planning PD
- What are the values of the district and school communities in which participants belong?
- What are factors that impact student learning that are most important to the participants?
- What key data points are needed to improve PD offerings?
- What constructs around equity should be measured to better understand if the PD affects teachers’ beliefs about each student’s ability to learn CS?
- From which other constructs that might impact student learning should data be collected?
Recommended Data Collection and Instrumentation
We recommend data be collected across four categories.
Key questions revolve around technical details of the evaluation process
- What data should be collected pre- and post-intervention or post-intervention only?
- How will PD providers ensure that even the least engaged in their PD offering provide data?
- For surveys, how long will the survey be? What trade-offs are there in time to take and complete the survey versus amount and type of data collected?
